|
| |
||||||
| ELECTRONIC EMG MANUAL® | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GUIDES & INFORMATION | ||
|
|
Electronic EMG Manual® | |
|
|
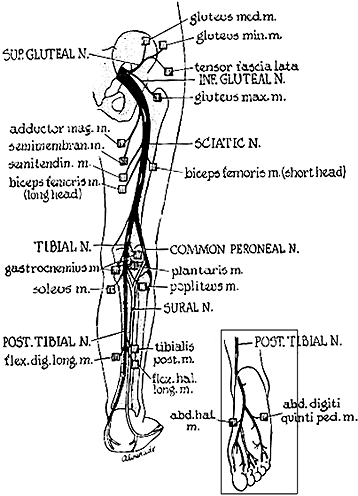
Peripheral Nerves Anatomy | |
|
|
General Muscles Anatomy | |
|
|
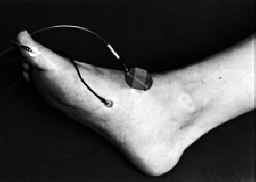
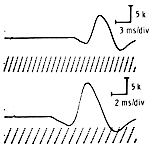
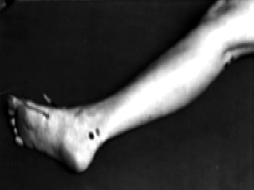
Nerve Conduction Set-Ups | |
|
|
Needle EMG Anatomy Atlas | |
|
|
Patient Education Series (FAQ) | |
|
|
Nerve Entrapment Guide | |
| Previous Chapter | Next Chapter |
|
This page was last updated on
Sunday, March 04, 2012
|
|
© Copyright 1997-2012
TeleEMG, LLC. All rights reserved
- TeleEMG is a Massachusetts Limited Liability Company (LLC)
|